S. aureus resistance is a pressing concern in modern medicine, highlighting the urgent challenge posed by this bacterium’s ability to develop multidrug resistance. Staphylococcus aureus, commonly associated with healthcare-associated infections, has shown alarming trends in tetracycline resistance, complicating treatment options. As healthcare providers increasingly consider doxycycline prophylaxis in specific populations, understanding the dynamics of resistance becomes critical. Recent clinical updates narrate how non-susceptibility to tetracycline among affected individuals is on the rise, often correlating with resistance to other key antibiotics. This resistance poses a significant threat to patient outcomes and underscores the necessity for diligent monitoring and innovative strategies in antibiotic usage to combat these resistant strains.
The challenges presented by Staphylococcus aureus drug resistance are reshaping clinical approaches in infectious disease management. As this pathogen becomes more adept at resisting treatments such as tetracycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, it’s vital for clinicians to stay informed on the latest findings regarding doxycycline as a prophylactic measure. Multidrug-resistant strains not only complicate treatment pathways but also necessitate enhanced surveillance to prevent the spread of infections. Understanding the current landscape of bacterial resistance will equip healthcare professionals with the tools needed to make informed decisions in patient care. Therefore, monitoring developments in research and antibiotic efficacy against such resistant organisms remains a priority for all in the medical field.
Understanding S. aureus Resistance in Clinical Settings
Staphylococcus aureus resistance ranks as one of the most pressing concerns in clinical microbiology today. Particularly, the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains presents significant challenges for healthcare providers. These resistant strains often exhibit decreased susceptibility to commonly used antibiotics, rendering many treatment options ineffective. A critical component of understanding this resistance is recognizing the various mechanisms employed by S. aureus to evade antimicrobial action. For instance, the production of beta-lactamases can disable penicillin antibiotics, while changes in membrane permeability can thwart the entry of antibiotics altogether.
The implications of S. aureus resistance extend beyond individual patient care, influencing broader public health strategies. As resistance patterns evolve, clinicians must adapt their treatment protocols to ensure effective management of infections. Monitoring local and regional trends in S. aureus resistance, particularly with respect to antibiotics such as tetracycline and doxycycline, is essential for informed clinical decision-making. Continuous education on emerging resistance patterns will facilitate targeted approaches, reducing the incidence of severe infections.
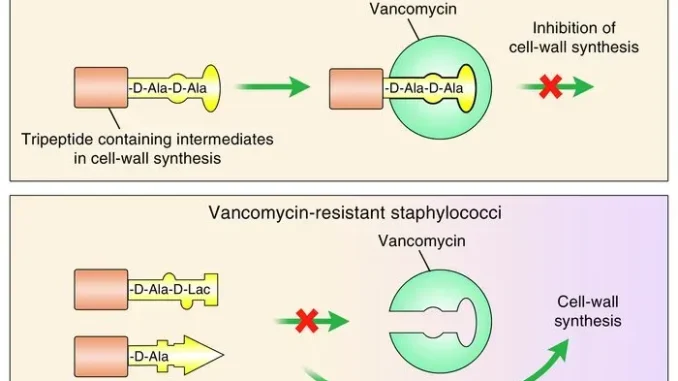
The Impact of Tetracycline Resistance on Doxycycline Prophylaxis
In recent studies, the prevalence of tetracycline resistance in Staphylococcus aureus has highlighted significant concerns for doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy-PEP) programs. In populations where Doxy-PEP is administered, non-susceptibility to tetracycline appears markedly pronounced. This resistance pattern not only complicates treatment strategies but also raises alarms about the effectiveness of doxycycline in preventing secondary infections among high-risk groups, such as men who have sex with men (MSM) engaged in certain activities.
The implications of this resistance are noteworthy; as doxycycline is commonly utilized for prophylaxis against bacterial infections, the co-resistance seen with other antibiotics such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole poses additional risks. Clinicians must remain vigilant and consider alternative strategies in light of these resistance patterns, particularly in managing infections sustained by multidrug-resistant S. aureus. Enhanced surveillance and research into effective alternatives for prophylaxis will be vital for maintaining effective public health responses.
Latest Clinical Updates on Staphylococcus aureus Infections
Ongoing clinical research has introduced critical insights into the management of Staphylococcus aureus infections. The increasing resistance of this pathogen has led to a paradigm shift in treatment strategies, compelling healthcare providers to adopt more targeted approaches. Recent studies presented in JID have documented the crucial findings regarding the effectiveness of specific antibiotic regimens against resistant S. aureus strains, emphasizing the role of personalized medicine in addressing the unique challenges posed by these infections.
Furthermore, the exploration of alternative therapeutic options, such as bacteriophage therapy and novel antimicrobial agents, reflects a progressive response to the challenge of multidrug resistance. The integration of genomics and molecular techniques in rapidly identifying resistant strains ensures timely interventions that can mitigate the spread and impact of infections. Clinicians must keep abreast of these clinical updates to effectively navigate the complexities associated with S. aureus resistance in their practice.
Laundry Practices and Their Role in Infection Control
With the emergence of infectious diseases like mpox, understanding effective laundry practices has gained importance in clinical settings. Laundry practices directly impact infection control, particularly in healthcare environments where contamination risks are heightened. Recent research has indicated that specific laundry procedures, including the use of sodium hypochlorite and high-temperature wash cycles, can effectively inactivate viruses like mpox, thereby reducing the transmission risk.
Additionally, it’s essential for healthcare professionals to familiarize themselves with best practices in laundry management to ensure fabric hygiene in clinical settings. Employing robust cleaning agents and maintaining optimal laundering conditions can play a pivotal role in curtailing the spread of infections. As infection control continues to be a priority, adopting evidence-based laundry practices will serve to protect both patients and healthcare workers alike.
HPV Prevalence Trends and Their Clinical Relevance
The decline in Human Papillomavirus (HPV) prevalence observed in recent studies provides critical insights for clinicians involved in cervical screening and vaccination initiatives. In Sweden, data from the National Cervical Screening Registry has demonstrated a remarkable decrease in HPV infections among vaccinated populations. Such findings reinforce the effectiveness of school-based vaccination programs in preventing HPV-related diseases.
Healthcare professionals must utilize this data to advocate for sustained HPV vaccination efforts, ensuring that future generations achieve similar protective benefits. As HPV remains a significant contributor to cervical cancer, understanding these trends assists clinicians in making informed recommendations for screening and preventive care, ultimately fostering better health outcomes in their patient populations.
Effectiveness of Vaccination Against Measles and Its Implications
Vaccination against measles has historically demonstrated high efficacy rates, a fact substantiated by recent findings that show the live attenuated vaccine can generate robust mucosal immunity. Understanding the pathway of the live attenuated virus to the respiratory tract sheds light on its mechanisms of action, crucial for communicating the importance of routine vaccinations to patients.
Clinicians should capitalize on these insights to educate individuals about the role of vaccination in community health. Emphasizing not only personal protection but also herd immunity is fundamental in combating preventable infectious diseases like measles. Integrating vaccination discussions into routine healthcare visits can significantly bolster community resilience against outbreaks.
The Role of Genetic Analysis in Monitoring Tick-borne Illnesses
Recent advancements in genomic research have transformed our understanding of tick-borne illnesses, such as Pacific Coast Tick Fever. The reclassification of the pathogen _Rickettsia rickettsii subsp Californica_ highlights the importance of genetic analysis in epidemiological studies. By employing detailed genomic evaluations, researchers can better elucidate taxonomy, pathogenesis, and transmission dynamics, enhancing the clinical management of these illnesses.
For healthcare providers managing tick-borne diseases, this knowledge allows for more accurate diagnostic practices and treatment strategies. Keeping informed about genetic developments not only aids in individual patient care but also shapes regional public health initiatives aimed at controlling tick populations and reducing disease incidence.
Practical Approaches to Enhance Patient Education on Infection Risks
Educating patients about the risks associated with infections, particularly those caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria like S. aureus, is integral to modern clinical practice. Effective patient education empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health and takes a proactive role in infection prevention. Utilizing clear, jargon-free language helps patients understand the significance of adhering to treatment protocols and the implications of antibiotic resistance.
Incorporating visual aids and real-life examples can further enhance understanding, making the information more relatable. By fostering open communication, clinicians can encourage patients to engage in discussions about their health, ultimately improving adherence to preventive measures and treatment regimens.
Future Directions in Antibiotic Resistance Research
As antibiotic resistance continues to escalate, innovative research directions are crucial for countering the challenges posed by resistant pathogens. Research into novel antibiotics and the mechanisms of resistance is paramount in developing effective treatments. Collaborative efforts from researchers, healthcare providers, and public health agencies are essential in fostering a multidisciplinary approach to understanding and mitigating resistance trends.
Additionally, investment in surveillance systems that track resistance patterns allows for a proactive stance in clinical management. By staying at the forefront of resistance research findings, clinicians can adapt their practices to ensure they remain effective in treating infections caused by resistant pathogens like S. aureus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Staphylococcus aureus resistance and why is it a concern?
Staphylococcus aureus resistance refers to the ability of the bacteria _S. aureus_ to survive exposure to antibiotics, making infections harder to treat. This resistance can arise through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations and horizontal gene transfer. The rise of multidrug-resistant strains poses significant challenges in clinical settings, leading to increased morbidity and treatment costs.
How does tetracycline resistance in Staphylococcus aureus affect treatment options?
Tetracycline resistance in _Staphylococcus aureus_ limits the effectiveness of this antibiotic class, which is commonly used for treating bacterial infections. As resistance rates rise, clinicians may need to consider alternative therapies or combinations of medications, underscoring the importance of susceptibility testing to guide effective treatment.
What role does doxycycline prophylaxis play in managing Staphylococcus aureus infections?
Doxycycline prophylaxis is utilized to prevent infections, particularly in high-risk populations. However, studies indicate that in some cases, recipients may carry strains of _Staphylococcus aureus_ that exhibit resistance, particularly to tetracycline and other antibiotics. Monitoring for resistance patterns is essential for optimizing doxycycline’s prophylactic use.
What are the implications of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical practice?
Multidrug-resistant _Staphylococcus aureus_ poses serious challenges in clinical settings, leading to limited treatment options and higher rates of treatment failure. Continuous surveillance and antibiotic stewardship are critical to manage these resistant strains effectively and to prevent their spread.
How can clinicians stay updated on Staphylococcus aureus resistance trends?
Clinicians can stay informed about Staphylococcus aureus resistance trends through ongoing educational resources such as publications from the Journal of Infectious Diseases, which regularly reports findings related to antibiotic resistance, including updates on tetracycline resistance and clinical management strategies.
| Title | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Rickettsia rickettsii subsp californica subsp nov, the Etiologic Agent of Pacific Coast Tick Fever | Identified the agent causing Pacific Coast tick fever, previously known as _Rickettsia 364D_. |
| Detection of Live Attenuated Measles Virus in the Respiratory Tract Following Subcutaneous Measles-Mumps-Rubella Vaccination | Demonstrated that the live measles vaccine travels to the respiratory tract, enhancing mucosal immunity. |
| Efficacy of Laundry Practices in Eliminating Mpox Virus From Fabrics | Sodium hypochlorite and specific laundry practices can effectively eliminate mpox virus from fabrics. |
| Population-Based Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of Declining Human Papillomavirus Prevalence | Significant decline in HPV16 and HPV18 prevalence among vaccinated women, indicating the vaccine’s effectiveness. |
| Staphylococcus aureus Tetracycline Resistance and Co-Resistance in a Doxycycline Postexposure Prophylaxis-Eligible Population | Higher tetracycline resistance in _S. aureus_ among those eligible for Doxy-PEP suggests multidrug resistance issues. |
Summary
S. aureus Resistance is a significant concern in the medical field, particularly as studies show an increasing prevalence of tetracycline resistance in populations at risk. Monitoring and understanding these trends are crucial, especially in the context of therapies like doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy-PEP). Ongoing research is essential to address the challenges posed by multidrug-resistant strains of _S. aureus_, ensuring that clinicians can effectively manage infections and preserve antibiotic efficacy.
Leave a Reply