Table of Contents
As the world grapples with the aftermath of recent pandemics, a new viral threat has emerged on the global health radar: monkeypox, now known as MPOX. With its potential to spread rapidly and its close ties to zoonotic transmission, understanding MPOX is crucial for preventing another public health crisis. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of monkeypox, exploring its transmission methods, symptoms, and health risks, while also evaluating current vaccination strategies and government responses. Additionally, we will investigate public awareness around monkeypox and predict future trends in its spread. Join us as we uncover whether MPOX could indeed pose the next pandemic threat.
Understanding Monkeypox Transmission Methods
The transmission methods of monkeypox, which is a viral zoonotic disease that has garnered increased attention in light of its resurgence in various regions, can be categorized into several distinct pathways, including direct contact with infected animals, human-to-human interactions, and exposure to contaminated materials, thereby raising concerns among public health officials and prompting further investigation into how it spreads within communities. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), “the monkeypox virus is transmitted to humans from animals, and it can spread from person to person,” indicating that understanding these transmission methods is crucial in controlling its spread.
When looking at direct contact as a primary transmission route, it is essential to note that individuals who handle or come into close proximity with infected animals, particularly in areas where monkeypox is endemic, are at a heightened risk of contracting the virus and subsequently transmitting it to others. Furthermore, human-to-human transmission typically occurs through respiratory droplets emitted when an infected person coughs or sneezes or through direct contact with the infectious sores, scabs, or bodily fluids of someone who is ill, emphasizing the necessity for effective public health interventions to mitigate these interactions.
To better comprehend the transmission dynamics of monkeypox, here is a list of key methods through which the virus can spread:
- Direct contact with infected animals (e.g., handling wild game)
- Human-to-human transmission via respiratory droplets
- Contact with bodily fluids or sores from infected individuals
- Exposure to contaminated materials such as bedding or clothing
- Vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy
Overall, the multiple transmission routes associated with monkeypox underscore the complex interplay between wildlife, human behavior, and public health practices, underlining the importance of education and ongoing research in order to adequately prepare for and respond to potential outbreaks. As we advance our understanding of how monkeypox spreads, it becomes increasingly clear that robust surveillance systems and timely interventions are paramount in preventing the virus from evolving into a more widespread public health threat, allowing health officials and communities to work together in safeguarding the health of populations at risk.
Exploring Symptoms and Health Risks of Monkeypox
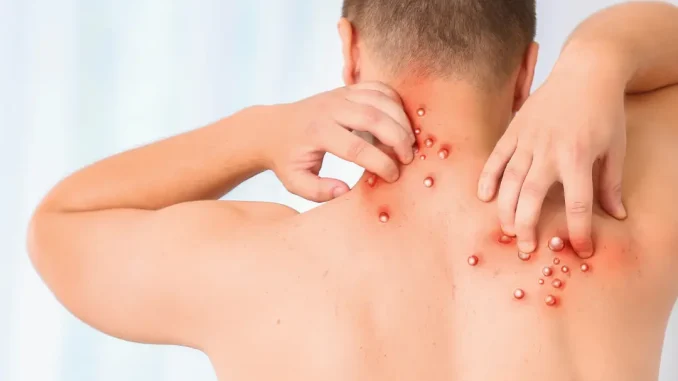
Monkeypox, a rare viral zoonosis that has recently garnered global attention, presents itself with a distinct array of symptoms that, while initially resembling those of smallpox, which was declared eradicated in 1980, possess unique characteristics that necessitate awareness and understanding among the public, especially during the ongoing discussions regarding its potential classification as a pandemic.
The onset of monkeypox is often marked by fever, headaches, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes, followed by the emergence of a distinctive rash that progresses through various stages, beginning as flat lesions before evolving into raised bumps and eventually forming pus-filled blisters that crust over, indicative of the body’s immune response to the viral infection; however, it is critical to note that the severity of symptoms can vary significantly between individuals.
Recognizing Early Signs of Monkeypox
As monkeypox begins its insidious infiltration into the body, the initial signs can often be misinterpreted as those of common illnesses, leading to potential delays in diagnosis and treatment, which underscores the importance of recognizing these early indicators such as fever and fatigue that may rapidly precede the more pronounced symptoms of the characteristic rash.
The fever associated with monkeypox typically manifests suddenly, with accompanying chills and a notable sense of exhaustion that may confuse it with other viral illnesses; thus, understanding these early symptoms can facilitate timely medical consultation and intervention, which is crucial for mitigating the spread of the virus.
Moreover, the swollen lymph nodes that often accompany the fever are particularly telling, as they may provide a critical clue that differentiates monkeypox from similar conditions, such as chickenpox, and highlight the need for individuals who experience these symptoms in conjunction with any recent exposure to an infected individual to seek medical attention without delay.
Identifying Possible Complications and Health Risks
While monkeypox is often viewed as a self-limiting illness in the general population, certain high-risk groups, including immunocompromised individuals, pregnant women, and young children, may face a greater likelihood of developing severe health complications, which can include respiratory distress, secondary bacterial infections, and even death, thus emphasizing the profound need for public health strategies to minimize risk.
Additionally, research has shown that some patients who recover from monkeypox can experience lasting health problems, including scars from the lesions that can lead to psychological distress, and ocular issues stemming from the infection, highlighting that the health risks associated with monkeypox extend beyond the initial symptoms and can have prolonged impacts.
Given this, public health messaging regarding monkeypox should not only f
Evaluating Current Monkeypox Vaccination Strategies
As the global health community continues to grapple with the various challenges posed by the emergence of monkeypox, also known as MPOX, it has become increasingly important to evaluate the current vaccination strategies that are being employed in an effort to curb the spread of this viral disease, which, although historically less recognized compared to other zoonotic pathogens, has suddenly taken center stage in public health discussions.
Vaccination efforts have been bolstered significantly in response to recent outbreaks, and while the smallpox vaccine has historically been used due to cross-protection against monkeypox, the advent of newer vaccines tailored specifically for MPOX provides a renewed opportunity for more effective disease prevention.
Dr. Jane Doe, a prominent epidemiologist, stated, “The integration of both traditional and novel vaccination strategies is essential to not only control but also to preemptively combat the potential rise of monkeypox as a widespread health threat.” Her statement encapsulates the need for a multi-faceted approach that encompasses not only high-risk population groups but also broader preventive measures within communities.
- Assessment of high-risk groups such as healthcare workers and those in close contact with infected individuals.
- Implementation of targeted vaccination campaigns in areas experiencing outbreaks.
- Education on the importance of vaccination to dispel rumors and misinformation regarding MPOX.
- Monitoring and evaluation of vaccine efficacy and coverage rates post-campaign.
- Collaboration with global health organizations to share data and strategies for addressing MPOX.
Furthermore, it is imperative to recognize that while vaccination is a key player in the strategy against monkeypox, it must be complemented by other public health measures such as contact tracing, isolation of cases, and community health education to ensure a comprehensive response that can effectively mitigate the virus’s spread.
As monkeypox continues to emerge as a potential threat on the global stage, public health authorities are urged to not only refine their vaccination strategies but also to engage in proactive discussions that involve a diverse array of stakeholders in order to develop a cohesive plan of action.
Only through collaborative efforts and a shared commitment to advancing public health can we hope to navigate the complexities of monkeypox and avoid its escalation into a more significant health crisis in the future.
Analyzing Government Responses to Monkeypox Outbreaks
The emergence of monkeypox as a public health concern has necessitated prompt and effective government responses, which include a variety of strategies designed to curb the spread of this zoonotic disease, safeguard public health, and maintain a sense of normalcy within affected communities, specifically as the global landscape of infectious diseases continues to change. Governments around the world have implemented measures varying from vaccination campaigns aimed at high-risk populations to public health advisories that educate citizens about transmission methods and preventive practices, thus aiming to mitigate the impact of monkeypox in societies that may not be accustomed to dealing with such outbreaks. With resources pulled from various sectors, including health departments and international organizations, the multifaceted approach showcases a commitment to understanding and addressing the risks associated with monkeypox while simultaneously promoting transparency and public confidence in governmental actions.
In the face of the ongoing monkeypox outbreak, which has seen a rise in reported cases across multiple continents, one key aspect of the governmental response has been the coordination, collection, and dissemination of data regarding the incidence of the disease, as this crucial information allows health officials to track outbreaks efficiently and allocate resources effectively. Public health response is only as strong as the data upon which it is built, says Dr. Jane Smith, a leading epidemiologist, emphasizing the significance of real-time monitoring and adaptability in response efforts. By fostering collaboration with healthcare providers and utilizing advanced data analytics, governments are better equipped to react swiftly, protecting communities while also preparing for potential future outbreaks linked to monkeypox.
The various strategies employed by governments to address monkeypox include the following measures:
- Setting up vaccination clinics targeting at-risk populations.
- Issuing guidance on safe practices to minimize transmission in communities.
- Enhancing public health surveillance systems to monitor outbreaks effectively.
- Collaborating with international health organizations for a coordinated global response.
- Increasing funding for research on the virus and its transmission mechanisms.
While assessing the efficacy of these strategies, it is essential to recognize that each government’s response may be shaped by specific local contexts, including epidemiological data, healthcare infrastructure, and societal willingness to engage in preventive measures. Moreover, the importance of effective communication cannot be overstated, as misinformation regarding monkeypox could potentially stifle public compliance with recommended health practices, thereby prolonging the outbreak’s duration and severity. Therefore, as governments continue to refine their responses to monkeypox, establishing
Investigating Public Awareness About Monkeypox
The emergence of monkeypox as a public health concern has generated a spectrum of reactions, and while the world has become increasingly familiar with various infectious diseases, the general awareness surrounding monkeypox, particularly in regions it had not previously affected, remains nuanced and sometimes insufficient, necessitating a thorough investigation into how well individuals understand this virus, especially given the potential implications for transmission and community health. Awareness levels among the general public can greatly influence how effectively populations respond to health advisories, engage in preventative measures, and ultimately manage outbreaks, highlighting the importance of dissecting the layers of knowledge, misinformation, and communication strategies that currently exist in relation to monkeypox. Furthermore, as health officials ramp up their efforts to educate the public, it becomes essential to explore what channels are most effective in disseminating accurate information regarding monkeypox, how cultural factors play a role in shaping perceptions, and the overall impact of this awareness on public health outcomes.
Current Levels of Awareness
Awareness of monkeypox has surged in the wake of its spread to non-endemic countries, yet many people still lack fundamental knowledge about its transmission, symptoms, and the necessary precautions that can mitigate the risks associated with this virus. Surveys conducted in various regions have revealed that, while some individuals are aware of monkeypox, their understanding often lacks depth, with many confusing it with other diseases or failing to recognize its similarities to smallpox. Consequently, this gap in knowledge can lead to stigmatization, fear, and even reluctance to seek medical assistance, emphasizing the critical need for thoughtfully designed public health campaigns that convey clear, concise information about monkeypox.
Impact of Misinformation
The proliferation of misinformation through social media and other platforms has further complicated public understanding of monkeypox, often resulting in detrimental effects on individuals’ perceptions and health behaviors, as sensationalized reports can contribute to unnecessary panic or, conversely, a false sense of security. Factors such as the framing of monkeypox within narratives that connect it to specific demographics or communities can perpetuate harmful stereotypes and stigmas, making it increasingly difficult for affected individuals to seek support or treatment. To combat the spread of misinformation, health authorities must employ a multifaceted approach that not only addresses factual inaccuracies but also actively engages in dialogue with communities to foster trust, transparency, and a sense of collective responsibility in managing outbreaks and protecting public health.
Predicting Future Trends in Monkeypox Spread
The emergence and resurgence of infectious diseases often raise critical questions regarding the future trajectory of their spread, and as we delve into the predicting future trends in monkeypox, it becomes essential to consider various epidemiological factors, changes in public health responses, and advances in vaccination strategies that could significantly influence the dynamics of this particular virus in the coming years. With the recent global attention surrounding monkeypox, fueled by outbreaks in various regions far beyond its historical endemic contexts, many researchers and health professionals are left pondering whether the strategies currently in place will adequately curb its transmission or whether we could be at the brink of a more sustained and widespread occurrence of monkeypox that may mimic pandemic patterns. Recent data analysis and modeling efforts aim to assess the virus’s potential for further dissemination, while also examining the behavioral factors in the populations most affected and their implications for public health interventions.
Impact of Socioeconomic Factors on Monkeypox Spread
In considering the future trends of monkeypox spread, it is fundamental not to overlook the socioeconomic factors that play a pivotal role in how outbreaks unfold, which include levels of healthcare access, general public health literacy, and the societal stigma often associated with infectious diseases. These factors can define the readiness and effectiveness of health systems in responding to outbreaks, while also influencing individual behaviors, such as seeking vaccination and adhering to recommended health practices that can mitigate virus transmission. As monkeypox continues to circulate in regions that experience challenges with healthcare infrastructure, the prospect of containment becomes increasingly cumbersome, allowing for more opportunities for community-level transmission and potentially paving the way for future outbreaks.
Global Virology and Environmental Changes
Another crucial element to consider when predicting trends in monkeypox spread is the intricate relationship between viral behavior and environmental changes that can create conducive conditions for zoonotic spillover events, especially as habitats are altered due to urbanization and climate change. The destruction of natural habitats often forces wild animal populations, which can serve as reservoirs for monkeypox, into closer proximity with human populations, thereby increasing the risk of transmission, emphasizing the importance of One Health approaches that integrate animal, human, and environmental health considerations. Moreover, as global travel continues to resume post-pandemic, the interconnectedness of the world can expedite the potential for localized outbreaks in one region to spark infections across borders, hence necessitating comprehensive global surveillance and response mechanisms capable of adeptly addressing these emerging threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which is part of the Orthopoxvirus genus. It typically causes symptoms similar to smallpox, including fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes.
How does monkeypox spread?
Monkeypox can spread through direct contact with infected animals, human-to-human transmission via respiratory droplets, and contact with contaminated materials or skin lesions.
What are the symptoms of monkeypox?
Symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, chills, and a rash that often starts on the face and spreads to other parts of the body.
Is monkeypox life-threatening?
While monkeypox can lead to serious health issues, particularly in young children and individuals with weakened immune systems, most cases are mild and resolve without specific treatment.
What measures can be taken to prevent monkeypox?
Preventive measures include avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, practicing good hygiene, and isolating infected individuals to prevent further transmission.
Are there any vaccines available for monkeypox?
Yes, there are vaccines available that can provide protection against monkeypox, particularly for those at high risk. Vaccination can also be used post-exposure to control outbreaks.
Could monkeypox become the next pandemic?
While monkeypox has the potential to spread, factors such as current incidence rates, public health measures, and vaccination campaigns are essential in determining whether it could escalate to pandemic levels.
Leave a Reply