The recent mpox outbreak has raised significant concern globally, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. First identified as monkeypox, this viral infection has shown a worrying resurgence, particularly in parts of Africa, with new cases emerging in countries like Burundi, Kenya, and Uganda. Understanding mpox symptoms, which range from fever and swollen lymph nodes to characteristic skin lesions, is crucial for effective prevention and management. Additionally, the virus’s transmission dynamics highlight the need for increased awareness and vaccination efforts, especially following the 2022 monkeypox outbreak that highlighted its spread through intimate contact. As we navigate this ongoing situation, finding effective mpox vaccines and addressing the risks associated with mpox variants are essential steps in curbing its impact.
The current surge of mpox cases, previously known as monkeypox, has sparked a renewed focus on this rare but dangerous viral infection. As health authorities work to understand the implications of this outbreak, exploring alternative terms like ‘monkeypox resurgence’ and ‘mpox infection’ allows for a broader discussion around its symptoms, transmission pathways, and available vaccines. The recent spike in cases, particularly in vulnerable populations, underscores the importance of public health measures and community awareness. With various mpox variants circulating, the need for effective intervention strategies is more critical than ever. Addressing this health crisis requires a concerted effort to educate the public about the disease and its prevention.
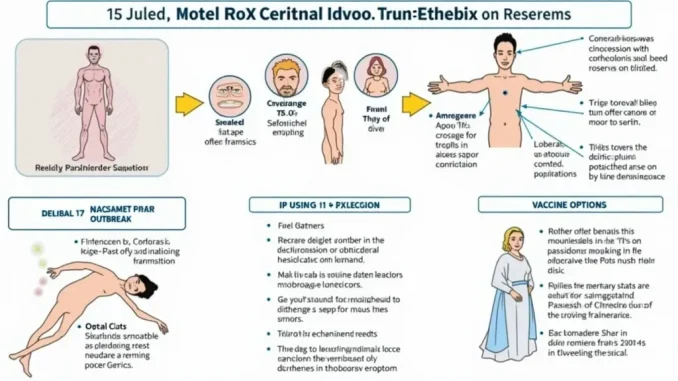
Understanding Mpox Symptoms
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, presents symptoms that can be alarming and often resemble those of chickenpox. Individuals infected with the virus may experience a range of symptoms, including fever, swollen lymph nodes, and a distinctive rash characterized by skin lesions. These lesions can develop into vesicles or boils, which are particularly contagious stages of the illness. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely intervention and management, especially given the recent uptick in cases.
In addition to the physical symptoms, there are psychological impacts associated with an mpox diagnosis. The stigmatization surrounding mpox, particularly in certain populations, can lead to anxiety and social withdrawal. As awareness of mpox symptoms increases, it is essential to foster a supportive environment for those affected, encouraging them to seek medical attention and access the appropriate treatments.
Transmission of Mpox: How Does It Spread?
Understanding how mpox is transmitted is vital to controlling its spread. The virus primarily spreads through direct contact with infected skin lesions, which can occur during intimate interactions. Notably, the 2022 global mpox outbreak highlighted how sexual transmission, particularly among men who have sex with men, played a significant role in the virus’s dissemination. Furthermore, mpox can also be transmitted from animals to humans, emphasizing the importance of monitoring animal populations in areas where the disease is endemic.
In addition to human-to-human and animal-to-human transmission, mpox can be spread through contaminated objects. Although the virus does not survive long on inanimate surfaces, recent contact with infected clothing or bedding can pose a transmission risk. This emphasizes the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures in environments where mpox cases are reported, particularly in healthcare settings and communal living spaces.
The Global Mpox Outbreak: Recent Developments
The recent declaration of mpox as a global health emergency by the World Health Organization underscores the seriousness of the outbreak. While cases have subsided in many regions, new infections continue to arise in parts of Africa, prompting concerns about the virus’s potential for resurgence. Countries are now being advised to enhance their surveillance and response strategies to prevent further spread and protect vulnerable populations.
The ongoing mpox outbreak serves as a reminder of the importance of global health preparedness. As new variants emerge, understanding their characteristics and potential risks is essential. This includes not only monitoring the transmission dynamics but also ensuring that vaccines are accessible and effective in preventing outbreaks. The global community must remain vigilant and responsive to these developments to mitigate the impact of mpox.
Vaccination Against Mpox: What You Need to Know
Vaccination plays a critical role in controlling the spread of mpox. The Jynneos vaccine has been shown to be effective in preventing infection from the virus, particularly following recent exposure. This vaccine is a vital tool in public health efforts, especially in populations at higher risk of infection, such as healthcare workers and individuals with potential exposure to infected individuals.
Despite the availability of the mpox vaccine, there are challenges in ensuring that it reaches those who need it most. Public health campaigns are necessary to educate communities about the benefits of vaccination and to address any concerns they may have. By increasing vaccine uptake, we can significantly reduce the incidence of mpox and prevent future outbreaks.
Identifying Mpox Variants: Clade 1 vs. Clade 2
Mpox has two primary variants, known as clade 1 and clade 2, each with distinct characteristics. Clade 1, which is more severe, has a higher fatality rate of approximately 3.6%. This variant is predominantly found in Central and East Africa and poses a significant threat to those without access to vaccines or antiviral treatments. On the other hand, clade 2 has a lower fatality rate and was responsible for the 2022 outbreak that spread globally.
Understanding these variants is crucial for public health responses, as they inform treatment protocols and vaccination strategies. Monitoring their prevalence and mutations can help predict potential outbreaks and guide resource allocation to areas most at risk. Continued research into the differences between these clades will enhance our ability to manage mpox effectively.
Risk Factors for Mpox Infection
Certain populations are at a higher risk of contracting mpox, particularly in regions where the disease is endemic. Vulnerable individuals living in high-density areas, such as refugee camps in Sub-Saharan Africa, face increased exposure to the virus due to limited access to healthcare and resources. These individuals often suffer from malnutrition, which can exacerbate the severity of mpox infections.
In contrast, in low-prevalence areas like the U.S., the risk of mpox infection remains relatively low. However, high-risk groups, such as immunocompromised individuals or those with underlying health conditions, should remain vigilant and take preventive measures. Understanding the demographics and risk factors associated with mpox infection is essential for targeted public health interventions.
Contagiousness of Mpox: When is it Most Infectious?
Mpox is most contagious during the later stages of infection, particularly when skin lesions are present. At this point, the risk of transmission is significantly heightened during direct contact, making it crucial for individuals with symptoms to isolate themselves and seek medical advice. Understanding when the virus is most infectious can aid in controlling its spread and protecting those who are at risk.
Moreover, the period of contagiousness emphasizes the need for effective public health messaging. Education about the stages of mpox, when to seek help, and how to prevent transmission can empower individuals to take necessary precautions. This knowledge is essential for reducing the risk of outbreaks and safeguarding community health.
Treatment Options for Mpox: What Works?
While most cases of mpox resolve without specific treatment, antiviral medications such as Tecovirimat (TPOXX) can mitigate symptoms and reduce the severity of the illness. These treatments are particularly important for individuals at higher risk of severe disease, as they can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Access to effective treatment options is crucial for controlling mpox outbreaks.
In addition to antiviral treatments, supportive care plays a vital role in the management of mpox. Ensuring that individuals have access to fluids, pain management, and medical support can significantly improve outcomes. Public health systems must be prepared to provide comprehensive care to those affected by mpox, ensuring that they receive the attention and treatment they need.
Conclusion: Addressing the Mpox Challenge
As the mpox outbreak continues to evolve, it is imperative for public health authorities and communities to remain vigilant. Awareness, education, and access to vaccines and treatments are essential components of an effective response. By addressing the challenges posed by mpox, we can work towards minimizing its impact and protecting vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, the recent developments surrounding mpox highlight the importance of global health preparedness and collaboration. As we navigate this public health challenge, it is crucial to invest in research, enhance surveillance, and ensure equitable access to vaccines and treatments to combat mpox effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary mpox symptoms to watch for during an outbreak?
Mpox symptoms can include fever, diarrhea, swollen lymph nodes, and distinctive skin lesions. Individuals experiencing these symptoms should seek medical attention, especially during an mpox outbreak.
How is mpox transmitted during the current outbreak?
Mpox is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected skin lesions or bodily fluids. The recent mpox outbreak has shown that it can also spread during sexual encounters, particularly among men who have sex with men. Additionally, contact with infected animals can lead to transmission.
Is there a vaccine available for the mpox outbreak?
Yes, there is a vaccine available for the mpox outbreak. The Jynneos vaccine is effective at preventing infection with mpox and is recommended for those at risk of exposure.
What are the risk factors associated with the mpox outbreak?
Individuals living in high-density areas where mpox is prevalent, such as refugee camps in Sub-Saharan Africa, are at greater risk. In the U.S., the risk remains low due to the availability of vaccines and antiviral treatments.
Can the mpox outbreak lead to severe illness or death?
While mpox has a lower mortality rate than smallpox, the clade 1 strain can have a fatality rate of up to 3.6%, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare and vaccinations. Prompt medical intervention can mitigate severe outcomes.
When is mpox most contagious during an outbreak?
Mpox is most contagious when individuals have visible skin lesions, such as vesicles or boils. It’s important to avoid close contact with infected individuals during this phase.
What treatments are available for mpox during an outbreak?
Most mpox cases resolve on their own, but antiviral treatment with medications like Tecovirimat (TPOXX) can help reduce symptom severity. Vaccination with Jynneos can also prevent future infections.
What should I do if I suspect I have mpox symptoms during the outbreak?
If you suspect you have mpox symptoms, it is crucial to isolate yourself and contact a healthcare provider for guidance. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the disease effectively.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of mpox | Mpox is a rare viral infection related to smallpox, characterized by symptoms like fever, swollen lymph nodes, and skin lesions. |
| WHO Declaration | The WHO declared mpox a global health emergency due to increased cases in Africa and the potential for further spread. |
| Variants of mpox | There are two strains: Clade 1 (more severe, 3.6% fatality) and Clade 2 (less severe, |
| Transmission | Spread occurs through contact with infected lesions, sexual encounters, and animal bites. Not typically airborne. |
| At-risk populations | Vulnerable individuals in high-density areas, refugees, and immunocompromised patients are at higher risk. |
| Mortality | While mpox has a lower mortality rate than smallpox, Clade 1 has a 3.6% fatality rate in the DRC. |
| Vaccination and Treatment | Jynneos vaccine is effective against mpox, and antivirals like Tecovirimat can reduce severity. |
Summary
The mpox outbreak is a significant global health concern that has gained attention due to its rapid spread and potential risks to public health. Understanding the nature of mpox, its variants, transmission methods, and at-risk populations is crucial for effective management and prevention. With the right measures, including vaccination and antiviral treatment, we can mitigate the impact of this viral infection.
Leave a Reply