Tecovirimat-resistant mpox has emerged as a concerning public health issue in the United States, with a recent cluster of cases highlighting the challenges posed by this drug-resistant variant of the monkeypox virus (MPXV). Health authorities have identified that all reported mpox cases in this cluster involved individuals with no documented history of prior tecovirimat treatment, raising alarm over the potential for drug resistance to develop. As tecovirimat has become the primary treatment option during the ongoing mpox outbreak, its effectiveness and safety are under scrutiny, particularly given its investigational status. Experts like Dr. Crystal M. Gigante emphasize the need for ongoing clinical trials to determine the true efficacy of tecovirimat against mpox, especially in patients with severe immunocompromising conditions. The emergence of resistant strains underscores the urgent need for alternative treatments and robust surveillance measures to manage and contain this evolving threat.
The recent identification of a monkeypox virus strain resistant to tecovirimat has raised significant concerns among health officials and researchers alike. This variant, which is part of the broader mpox outbreak, presents challenges in effective management and treatment options. With instances of drug-resistant monkeypox increasing, the medical community is urged to explore and develop new therapeutic avenues. The implications of tecovirimat resistance highlight the importance of understanding the disease’s dynamics and the need for innovative approaches in monkeypox treatment. As mpox cases continue to evolve, researchers are focusing on the development of alternative strategies to combat this persistent and adaptive viral threat.
Understanding Tecovirimat-Resistant Mpox
The emergence of tecovirimat-resistant mpox cases marks a troubling development in the ongoing fight against monkeypox. This newly identified variant of the virus has been linked to clusters of infections across the United States, raising alarms within the public health community. The CDC has noted that these cases occurred in individuals with no prior history of tecovirimat treatment, suggesting that resistance can develop even without previous exposure to the drug. This situation highlights the potential for drug resistance to complicate the management of mpox outbreaks and necessitates a reevaluation of current treatment protocols.
As mpox cases continue to rise globally, the identification of a tecovirimat-resistant variant could pose significant challenges for healthcare providers. The efficacy of tecovirimat, which has been widely used under compassionate use protocols, is now under scrutiny. Experts emphasize that while tecovirimat may be safe, its effectiveness against this resistant strain remains uncertain. Continued surveillance and research into alternative treatment options are crucial to ensuring effective care for patients, particularly those with compromised immune systems.
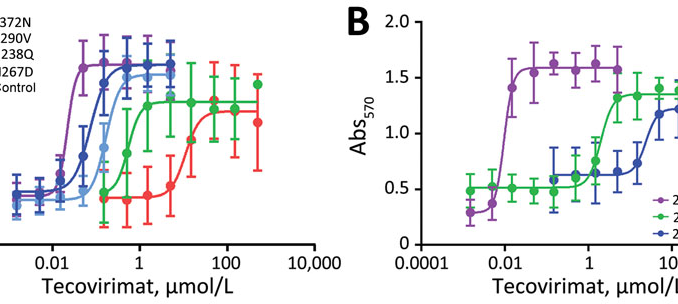
The Impact of Mutations on Mpox Outbreaks
Mutations in the monkeypox virus, particularly those associated with drug resistance, pose a serious threat to public health efforts. The recent report documenting F13 mutations across multiple states underscores the need for comprehensive genomic surveillance. These mutations, identified in a small cluster of patients, indicate a potential trend of increasing drug resistance that could hinder treatment efforts. With the ongoing mpox outbreak, understanding the genetic evolution of the virus is essential to develop effective strategies for managing and preventing further spread.
The combination of F13 mutations found in 18 patients from various U.S. states reflects an emerging pattern that could complicate outbreak responses. Public health experts are concerned that without proper monitoring and sequencing of mpox cases, the true scale of drug-resistant variants may remain hidden. This lack of visibility can lead to inadequate responses and treatments for patients, particularly those who are at higher risk for severe disease. As mpox continues to evolve, proactive measures in genomic surveillance and data collection will be vital for informing treatment decisions and public health strategies.
Current Challenges in Monkeypox Treatment
The ongoing mpox outbreak has highlighted significant challenges in the treatment landscape, particularly regarding the reliance on tecovirimat. While this antiviral has been a frontline treatment, its investigational status and the recent emergence of resistance raise critical questions about its long-term viability. The CDC’s warning about the investigational use of tecovirimat emphasizes the need for healthcare providers to remain vigilant and consider alternative therapies for patients, especially those with severe immunocompromising conditions.
Moreover, the limited approved therapeutic options for mpox underscore the urgency for research into alternative treatments. The reported cases of tecovirimat-resistant mpox infection illustrate the potential inadequacies in current treatment protocols. Public health officials urge continued clinical trials, such as the NIH’s STOMP study, to explore the efficacy of tecovirimat and other treatments. Identifying safe and effective alternatives will be crucial in managing future outbreaks and ensuring positive patient outcomes.
Monitoring Mpox Variants: A Public Health Priority
The identification of a tecovirimat-resistant monkeypox virus variant has brought to light the importance of monitoring viral mutations as part of public health efforts. As illustrated by the recent findings across several states, genomic surveillance allows health authorities to track the emergence of resistant strains, which is critical for timely intervention. The ability to detect such mutations can help inform treatment protocols and public health responses to ensure that patients receive the most effective care possible.
In addition to monitoring resistance, public health laboratories play a vital role in understanding the broader epidemiology of mpox. Continuous genomic sequencing can provide insights into transmission patterns and the potential for further resistance development. As the landscape of mpox evolves, maintaining robust surveillance systems will be essential in safeguarding public health and preventing outbreaks from spiraling out of control.
The Role of Clinical Trials in Mpox Management
Clinical trials are essential in determining the efficacy and safety of treatments for mpox, particularly as drug resistance becomes a growing concern. The ongoing STOMP trial, for instance, aims to assess the effectiveness of tecovirimat in managing mpox cases, including those presenting with drug-resistant variants. This research is crucial not only for understanding how tecovirimat performs in real-world scenarios but also for identifying which patient populations may benefit most from existing therapies.
Moreover, the data collected from clinical trials will inform future treatment guidelines and public health policies. With the emergence of tecovirimat-resistant mpox, there is an urgent need for comprehensive research that evaluates various treatment options. Engaging healthcare providers and patients in these trials can lead to better outcomes and a more nuanced understanding of how to approach mpox management in the face of evolving viral challenges.
Public Awareness and Education on Mpox
Public awareness plays a critical role in managing mpox cases and preventing future outbreaks. Educating communities about the symptoms, transmission, and treatment options available can empower individuals to seek timely medical assistance and reduce stigma associated with the disease. As cases of tecovirimat-resistant mpox emerge, it becomes even more important to inform the public about the evolving nature of the virus and the need for ongoing vigilance.
Health authorities can leverage various platforms to disseminate information regarding mpox, including social media, community events, and healthcare provider outreach. By fostering a better understanding of mpox and its implications, communities can be better prepared to respond to outbreaks. Additionally, increasing awareness about clinical trials and encouraging participation can lead to advancements in treatment options for mpox, benefiting future patients.
Evolving Strategies for Monkeypox Prevention
As the mpox outbreak evolves, so too must the strategies for prevention and management. The emergence of tecovirimat-resistant variants has prompted public health officials to reconsider existing prevention measures, including vaccination and community engagement strategies. While vaccines have been effective in reducing the spread of monkeypox, there is a growing need to enhance educational efforts to ensure that at-risk populations are informed about the risks and available preventive measures.
In addition to vaccination, public health campaigns should focus on promoting safe practices and encouraging individuals to seek medical care if they exhibit symptoms. Engaging with community leaders and organizations can also help to disseminate critical information and strengthen community resilience against mpox outbreaks. As strategies for prevention evolve in response to new data, ongoing collaboration between public health authorities, healthcare providers, and the community will be vital in controlling the spread of the disease.
Future Directions in Mpox Research
The ongoing research into mpox and its treatment options is crucial for addressing the challenges posed by drug-resistant strains. As scientists continue to study the genetic mutations associated with tecovirimat resistance, it is essential to explore the development of new antiviral agents and treatment modalities. This research will not only help to combat the current mpox outbreak but also prepare for potential future outbreaks of the disease.
Furthermore, funding and support for mpox research must be prioritized to ensure that effective treatments are available. Collaborative efforts between public health organizations, academic institutions, and pharmaceutical companies will be vital in advancing the understanding of monkeypox and developing innovative solutions. As the landscape of mpox evolves, a robust research agenda will be key to mitigating the impact of drug-resistant variants and improving public health outcomes.
The Importance of Genomic Surveillance in Mpox Control
Genomic surveillance is an indispensable tool in controlling mpox outbreaks, particularly in the context of emerging drug-resistant variants. By sequencing viral samples from mpox cases, public health officials can monitor the evolution of the virus and identify mutations that may confer resistance to treatment. This information is critical for guiding therapeutic decisions and implementing timely public health interventions.
Moreover, the findings from genomic surveillance can inform vaccine development and optimization. Understanding the genetic makeup of circulating mpox strains allows researchers to tailor vaccines and improve their efficacy against the most prevalent variants. As mpox continues to pose a threat to public health, investing in genomic surveillance will be essential for early detection of resistance patterns and for ensuring the effectiveness of current and future treatments.
Community Engagement in Mpox Prevention Efforts
Community engagement is vital in the fight against mpox, particularly as the virus continues to evolve and adapt. By involving local communities in prevention efforts, public health authorities can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards managing the spread of the disease. Collaborative initiatives that promote education and awareness can empower individuals to take proactive steps in protecting themselves and their neighbors from mpox.
Additionally, community partnerships can facilitate the dissemination of information about clinical trials and new treatment options for mpox. Engaging community leaders and organizations can help to reach diverse populations and ensure that information is accessible to all. As public health strategies evolve in response to the emergence of tecovirimat-resistant mpox, community involvement will be crucial in creating effective prevention and response plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tecovirimat-resistant mpox and why is it a concern?
Tecovirimat-resistant mpox refers to monkeypox cases caused by a variant of the virus (MPXV) that has developed resistance to tecovirimat, the primary treatment used during the ongoing mpox outbreak. This resistance raises concerns about the effectiveness of current treatments, particularly since the emergence of such variants could limit options for managing severe cases.
How common are tecovirimat-resistant mpox cases in the current outbreak?
The emergence of tecovirimat-resistant mpox cases appears to be rare, with reports indicating a cluster of cases identified in the United States. However, genomic surveillance suggests that the actual incidence may be underreported, as not all mpox samples are sequenced.
Why is tecovirimat not FDA-approved for mpox treatment?
Tecovirimat is not FDA-approved for mpox treatment because it has been made available through compassionate use amid the ongoing outbreak. Its safety and effectiveness for mpox are still under review, prompting health authorities to treat its use as investigational.
What are the implications of using tecovirimat for mpox treatment?
Using tecovirimat for mpox treatment carries the risk of developing drug-resistant variants, particularly if used excessively. Health officials recommend careful monitoring and suggest that further clinical trials are necessary to better understand its efficacy and safety for mpox patients.
Are there alternatives to tecovirimat for treating mpox?
Currently, there are limited approved therapeutic options for mpox beyond tecovirimat. The CDC emphasizes the need for developing alternative treatments and ongoing surveillance to ensure effective management of mpox cases, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
How can the public health system monitor tecovirimat-resistant mpox variants?
Public health laboratories conduct genomic surveillance of mpox cases, which is essential for detecting and monitoring the spread of tecovirimat-resistant variants. This ongoing surveillance helps inform treatment strategies and public health responses.
What should healthcare providers inform patients about tecovirimat and mpox treatment?
Healthcare providers should inform mpox patients about the investigational nature of tecovirimat, its potential effectiveness, and the availability of clinical trials, such as the STOMP study, which aims to assess tecovirimat’s efficacy in various patient populations.
What role does tecovirimat play in treating severe mpox cases?
While tecovirimat is considered generally safe, its effectiveness in treating severe mpox cases remains uncertain, particularly for immunocompetent patients. Ongoing research is needed to clarify who benefits most from this treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Identification of Cases | A cluster of mpox cases caused by a tecovirimat-resistant monkeypox virus has been found in the U.S. |
| Concerns Over Resistance | The emergence of a drug-resistant variant raises issues as no prior treatment history with tecovirimat was documented in affected individuals. |
| Ongoing Clinical Trials | Studies, including the NIH STOMP trial, are assessing the efficacy of tecovirimat for treating mpox. |
| Need for Alternatives | Health authorities are emphasizing the necessity for additional treatment options and ongoing surveillance for mpox. |
| Genomic Surveillance | Public health laboratories are conducting surveillance to monitor the spread of tecovirimat-resistant variants. |
Summary
Tecovirimat-resistant mpox presents a significant challenge in managing monkeypox outbreaks. The recent identification of a cluster of cases in the U.S. has highlighted the potential risks associated with drug-resistant variants of the virus, particularly as no prior tecovirimat treatments were reported among affected individuals. The emergence of such variants underscores the urgent need for alternative therapeutic options and robust surveillance to effectively manage future outbreaks. Continued research and clinical trials will be crucial in determining the best strategies for treating mpox and safeguarding public health.
Leave a Reply